Aerolpane
Components-Wing
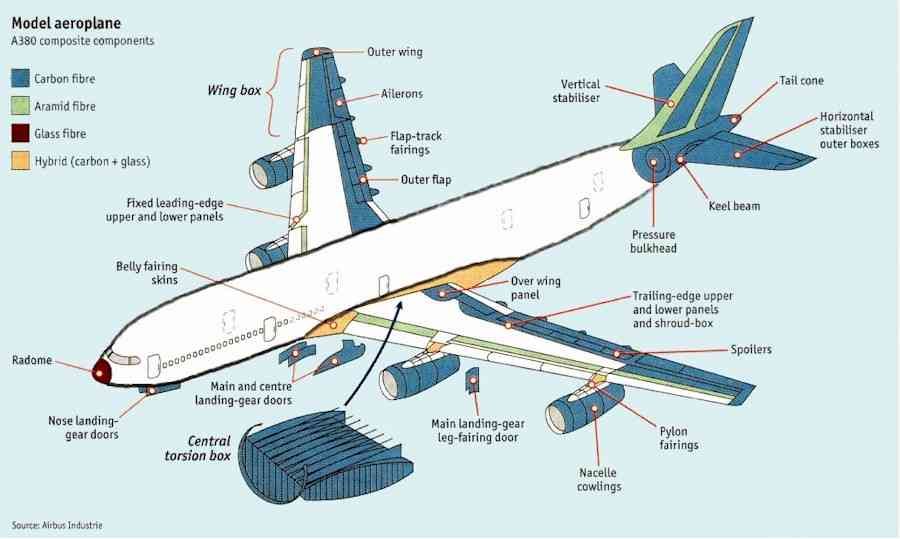
A wing is a type of a fin with a surface that produces aerodynamic force for flight or propulsion through the atmosphere. As such, wings have an airfoil shape, a streamlined cross-sectional shape producing lift. Air that travels over the top surface of the airfoil has to travel fster and thus gains dynamic pressure. The pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces is called lift and opposes the weight of the aircraft.
Types of Aircrafts
Propellar Aircrafts
Use one or more propellers (airscrews) to create thrust in a forward direction. The propeller is usually mounted in front of the power source in tractor configuration but can be mounted behind in pusher configuration. Variations of propeller layout include contra-rotating propellers and ducted fans.
Jet Aircraft
Use airbreathing jet engines, which take in air, burn fuel with it in a combustion chamber, and accelerate the exhaust rearwards to provide thrust. Turbojet and turbofan engines use a spinning turbine to drive one or more fans, which provide additional thrust. An afterburner may be used to inject extra fuel into the hot exhaust, especially on military "fast jets". Use of a turbine is not absolutely necessary: other designs include the pulse jet and ramjet. These mechanically simple designs cannot work when stationary, so the aircraft must be launched to flying speed by some other method. Other variants have also been used, including the motorjet and hybrids such as the Pratt & Whitney J58, which can convert between turbojet and ramjet operation.
Rotor Craft
Some rotorcraft, such as helicopters, have a powered rotary wing or rotor, where the rotor disc can be angled slightly forward so that a proportion of its lift is directed forwards. The rotor may, like a propeller, be powered by a variety of methods such as a piston engine or turbine. Experiments have also used jet nozzles at the rotor blade tips.
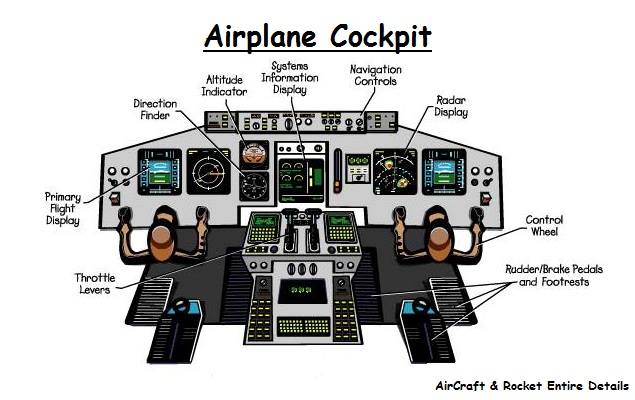
Flight Control